How to write a C Program to Count Total Notes in a Given Amount with an example using For Loop, Functions, and If Statement.
C Program to Count Total Notes in a Given Amount Example 1
This program helps the user to enter the amount of cash, and then it’s going to find the total number of denominators using For Loop
/* C Program to Count Total Notes in a Given Amount */
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a[8] = {500, 100, 50, 20, 10, 5, 2, 1};
int Amount, i, temp;
printf("\n Please Enter the Amount of Cash = ");
scanf("%d", &Amount);
temp = Amount;
for(i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
printf("\n %d Notes is = %d", a[i], temp / a[i]);
temp = temp % a[i];
}
return 0;
}
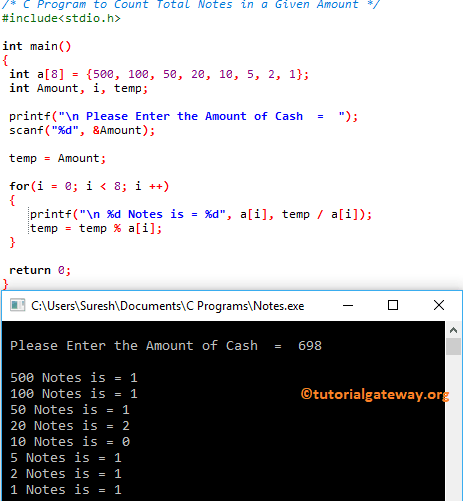
For Loop First Iteration : for(i = 0; 0 < 8; 0++)
a[i] = a[0] = 500
temp / a[i] = 698 / 500 = 1
Next, temp = 698 % 500 = 198
Now temp = 198, and i value will be incremented to 1
For Loop Second Iteration : for(i = 1; 1 < 8; 1++)
a[i] = a[1] = 100
temp / a[i] = 198 / 100 = 1
Next, temp = 198 % 100 = 98
Now temp = 98, and i value will be incremented to 1
Third Iteration : for(i = 2; 2 < 8; 2++)
a[i] = a[2] = 50
temp / a[i] = 98 / 50 = 1
Next, temp = 98 % 50 = 48
Now temp = 48, and i value will be 3
Fourth Iteration : for(i = 3; 3 < 8; 3++)
a[i] = a[3] = 20
temp / a[i] = 48 / 20 = 2
Next, temp = 48 % 20 = 8
Now temp = 8, and i value will be 4
Fifth Iteration : for(i = 4; 4 < 8; 4++)
a[i] = a[4] = 10
temp / a[i] = 8 / 10 = 0
Next, temp = 8 % 10 = 8
Now temp = 8, and i value will be 5
Do the same for remaining C Programming iterations
C Program to Count Total Notes in a Given Amount Example 2
It is the same program that we used in the first example, but this time we separated the logic using Functions.
/* C Program to Count Total Notes in a Given Amount */
#include<stdio.h>
void Total_Notes(int Amount);
int main()
{
int Amount;
printf("\n Please Enter the Amount of Cash = ");
scanf("%d", &Amount);
Total_Notes(Amount);
return 0;
}
void Total_Notes(int Amount)
{
int a[8] = {500, 100, 50, 20, 10, 5, 2, 1};
int i, temp;
temp = Amount;
for(i = 0; i < 8; i ++)
{
printf("\n %d Notes is = %d", a[i], temp / a[i]);
temp = temp % a[i];
}
}
Please Enter the Amount of Cash = 1568
500 Notes is = 3
100 Notes is = 0
50 Notes is = 1
20 Notes is = 0
10 Notes is = 1
5 Notes is = 1
2 Notes is = 1
1 Notes is = 1Program to Count Total Notes in a Given Amount Example 3
I know this is a horrible idea, but it is good to know that you can achieve this using the If statement. Here, for every If statement, the amount will be reduced.
/* C Program to Count Total Notes in a Given Amount */
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int Amount;
int Note500, Note100, Note50, Note20, Note10, Note5, Note2, Coin1;
Note500 = Note100 = Note50 = Note20 = Note10 = Note5 = Note2 = Coin1 = 0;
printf("\n Please Enter the Amount of Cash = ");
scanf("%d", &Amount);
if (Amount > 500)
{
Note500 = Amount / 500;
Amount = Amount - (Note500 * 500);
}
if (Amount >= 100)
{
Note100 = Amount / 100;
Amount = Amount - (Note100 * 100);
}
if (Amount >= 50)
{
Note50 = Amount / 50;
Amount = Amount - (Note50 * 50);
}
if (Amount >= 20)
{
Note20 = Amount / 20;
Amount = Amount - (Note20 * 20);
}
if (Amount >= 10)
{
Note10 = Amount / 10;
Amount = Amount - (Note10 * 10);
}
if (Amount >= 5)
{
Note5 = Amount / 5;
Amount = Amount - (Note5 * 5);
}
if (Amount >= 2)
{
Note2 = Amount / 2;
Amount = Amount - (Note2 * 2);
}
if (Amount >= 1)
{
Coin1 = Amount;
}
printf("\n Total Number of Notes presenet in the Cash that you entered are \n");
printf("\n 500 Notes = %d", Note500);
printf("\n 100 Notes = %d", Note100);
printf("\n 50 Notes = %d", Note50);
printf("\n 20 Notes = %d", Note20);
printf("\n 10 Notes = %d", Note10);
printf("\n 5 Notes = %d", Note5);
printf("\n 2 Notes = %d", Note2);
printf("\n 1 Coin = %d", Coin1);
return 0;
}
Please Enter the Amount of Cash = 259876
Total Number of Notes presenet in the Cash that you entered are
500 Notes = 519
100 Notes = 3
50 Notes = 1
20 Notes = 1
10 Notes = 0
5 Notes = 1
2 Notes = 0
1 Coin = 1